Sun Yat-sen University
Sun Yat-sen University
Sun Yat-sen University
Sun Yat-sen University
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition 2025
*Equal Contribution, †Corresponding Author

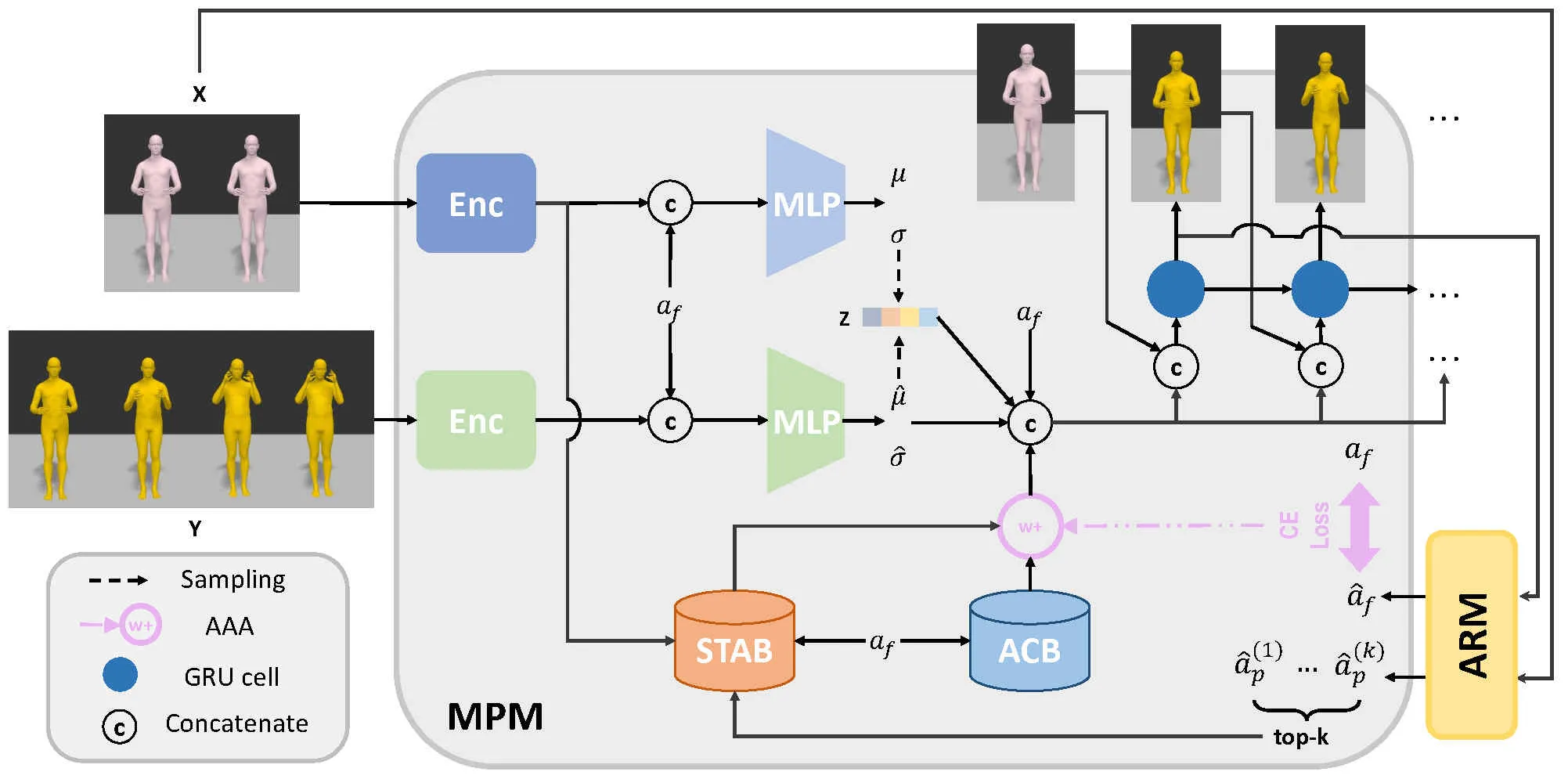
Action-driven stochastic human motion prediction aims to generate future motion sequences of a pre-defined target action based on given past observed sequences performing non-target actions. This task primarily presents two challenges. Firstly, generating smooth transition motions is hard due to the varying transition speeds of different actions. Secondly, the action characteristic is difficult to be learned because of the similarity of some actions. These issues cause the predicted results to be unreasonable and inconsistent. As a result, we propose two memory banks, the Soft-transition Action Bank (STAB) and Action Characteristic Bank (ACB), to tackle the problems above. The STAB stores the action transition information. It is equipped with the novel soft searching approach, which encourages the model to focus on multiple possible action categories of observed motions. The ACB records action characteristic, which produces more prior information for predicting certain actions. To fuse the features retrieved from the two banks better, we further propose the Adaptive Attention Adjustment (AAA) strategy. Extensive experiments on four motion prediction datasets demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms the previous state-of-the-art.